How to operate a drone safely and effectively is crucial for both recreational and professional users. This guide delves into the essential components, pre-flight procedures, flight controls, and photography techniques, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of this increasingly popular technology. We’ll explore everything from understanding your drone’s mechanics to mastering aerial maneuvers and adhering to safety regulations. Whether you’re a novice pilot or seeking to refine your skills, this resource will equip you with the knowledge needed to confidently take to the skies.
We will cover a wide range of topics, from the basics of drone components and their functions to advanced techniques in aerial photography and videography. Safety and legal compliance will be emphasized throughout, ensuring a responsible and enjoyable drone flying experience.
Understanding drone operation involves familiarizing yourself with its controls and safety protocols. A crucial step is learning about pre-flight checks and understanding airspace regulations. For comprehensive guidance, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone before your first flight. This will help ensure you operate your drone safely and responsibly, ultimately leading to a positive flying experience.
Drone Components and Their Functions
Understanding the individual components of a drone and their functions is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section details the key parts of a typical drone, their roles, and variations.
Drone Propellers and Motors
Propellers generate the thrust necessary for flight. Different propeller designs impact flight characteristics. Larger propellers generally provide more lift and slower speeds, while smaller propellers offer higher speeds and quicker maneuverability. Propeller pitch also influences performance; a higher pitch yields more thrust but lower speed. These propellers are driven by electric motors, typically brushless DC motors, known for their efficiency and longevity.
The number of motors (typically 4) dictates the drone’s stability and redundancy.
Flight Controller and GPS
The flight controller is the drone’s “brain,” managing all aspects of flight. It receives data from various sensors (accelerometers, gyroscopes, barometers) and uses algorithms to maintain stability and execute commands. The GPS module provides location data, enabling features like autonomous flight, return-to-home (RTH), and geofencing. A high-quality GPS signal is essential for accurate positioning and safe operation.
Drone Batteries
Lithium Polymer (LiPo) batteries are the standard power source for most drones due to their high energy density and lightweight nature. However, LiPos require careful handling and storage due to their flammability. Other battery types, such as lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries, offer improved safety but often at the cost of lower energy density. The choice of battery type depends on the drone’s size, flight time requirements, and safety priorities.
LiPo batteries are known for their high energy density, making them ideal for drones needing extended flight times. However, they are sensitive to overcharging, discharging, and extreme temperatures. LiFePO4 batteries, while offering better safety and longer lifespan, typically have lower energy density and might result in shorter flight times.
Drone Camera
The camera is a key feature for many drone users, enabling aerial photography and videography. Camera specifications, such as resolution, sensor size, and lens capabilities, vary widely across drone models. Features like electronic image stabilization (EIS) and mechanical gimbal stabilization further enhance image quality and reduce video shake.
Drone Model Comparison
| Model | Battery Life (minutes) | Camera Resolution (MP) | Max Flight Time (minutes) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DJI Mavic 3 | 46 | 20 | 46 |
| Autel Evo II Pro | 40 | 48 | 40 |
| Skydio 2 | 27 | 12.6 | 27 |
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight inspection is essential for ensuring safe and legal operation. This involves a series of checks to verify the drone’s functionality and environmental conditions.
Pre-Flight Checklist
A comprehensive pre-flight checklist should include:
- Battery level check
- Propeller inspection for damage
- Gimbal and camera functionality test
- GPS signal strength verification
- Compass calibration
- Reviewing local regulations and airspace restrictions
- Checking weather conditions
Compass and Sensor Calibration
Calibrating the drone’s compass and other sensors is crucial for accurate flight and stability. This process ensures that the drone’s internal orientation is correctly aligned with the Earth’s magnetic field and other environmental factors. Inaccurate calibration can lead to erratic flight behavior and potential accidents.
GPS Signal Verification
Before takeoff, verify a strong GPS signal and sufficient satellite lock. The number of satellites needed for stable flight varies depending on the drone model, but generally, a minimum of 6-8 satellites is recommended. A weak GPS signal can lead to inaccurate positioning and loss of control.
Pre-Flight Inspection Flowchart
A visual flowchart helps ensure all pre-flight checks are completed systematically. The flowchart would include steps such as power-on self-tests, visual inspection of the drone, battery level check, GPS signal verification, compass calibration, and final pre-flight checks before initiating the flight.
Taking Off and Landing
Safe and controlled takeoff and landing procedures are paramount for preventing accidents. Different techniques exist, depending on the environment and drone capabilities.
Takeoff and Landing Techniques
Common takeoff methods include assisted takeoff (using automated features), manual takeoff (requiring more pilot skill), and launching from hand. Landing procedures generally involve a gradual descent, aiming for a smooth and controlled touchdown. Different landing techniques are used depending on the terrain, wind conditions, and the presence of obstacles.
Safety Procedures in Various Environments
Windy conditions necessitate careful maneuvering during takeoff and landing. In confined spaces, extra caution is needed to avoid collisions. Best practices include selecting a location with minimal wind and sufficient space for maneuvering.
Low Battery Landing Procedures
When the battery is low, initiate a return-to-home (RTH) function if available. If RTH is unavailable, perform a controlled descent, prioritizing a safe landing over maintaining altitude or position.
Step-by-Step Takeoff and Landing Guide
- Power on the drone and controller.
- Verify GPS signal and compass calibration.
- Perform a pre-flight check of propellers and other components.
- Initiate takeoff using the chosen method (assisted or manual).
- Maintain stable hover before initiating any maneuvers.
- For landing, initiate a slow and controlled descent.
- Touch down gently on a stable surface.
- Power off the drone and controller.
Drone Flight Controls and Maneuvers: How To Operate A Drone
Understanding drone flight controls is essential for safe and precise maneuvering. This section covers the basic controls and common flight modes.
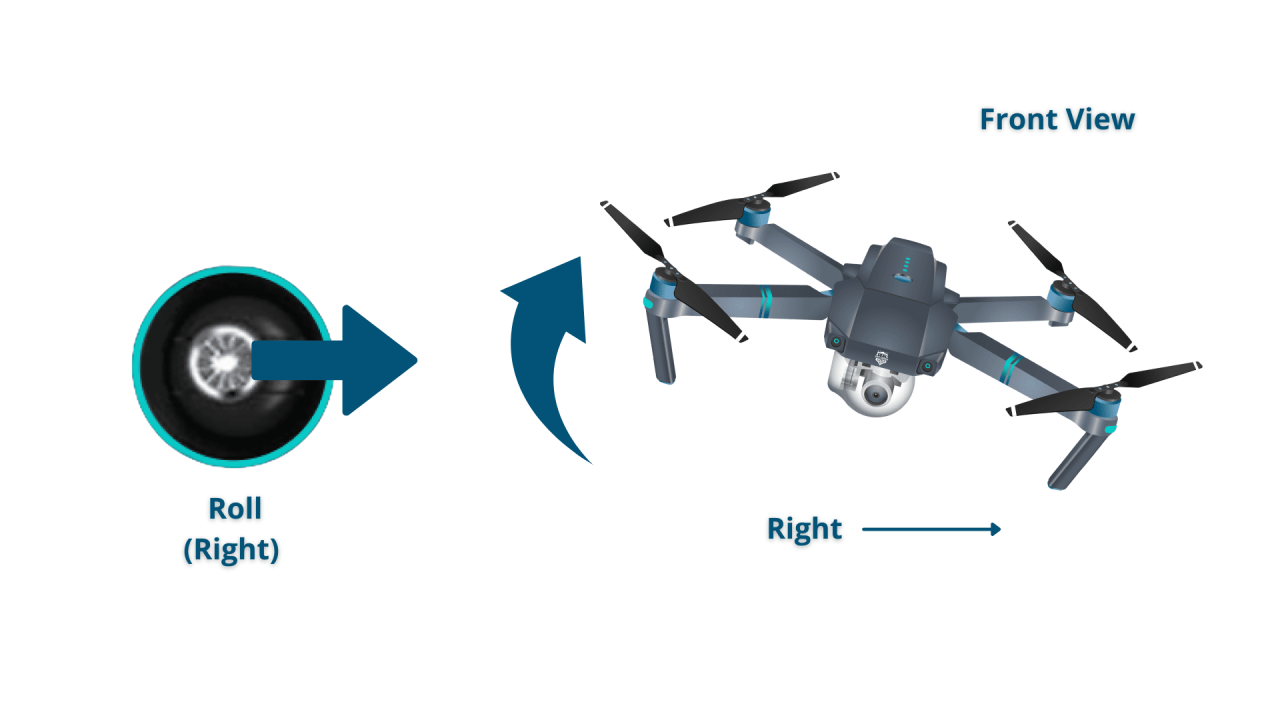
Drone Control Sticks
Most drones use two control sticks: one for pitch and roll (forward/backward and left/right movement), and the other for yaw (rotation) and throttle (altitude control). The precise function of each stick can vary slightly between drone models.
Drone Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of automation and pilot control. GPS mode relies on GPS data for stability, while Attitude mode relies on onboard sensors. Manual mode offers full control but requires more skill.
Basic Drone Maneuvers, How to operate a drone
Basic maneuvers include hovering, moving forward/backward, turning, and side-to-side movement. Mastering these fundamental maneuvers is crucial before attempting more advanced techniques.
Tips for Improving Drone Piloting Skills
- Practice regularly in a safe and open area.
- Start with basic maneuvers and gradually increase complexity.
- Utilize simulator software to hone skills in a risk-free environment.
- Understand the limitations of your drone and your own piloting abilities.
- Always prioritize safety and responsible operation.
Drone Photography and Videography
Capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos requires understanding camera settings, composition, and flight techniques.
Adjusting Camera Settings
Camera settings like ISO, shutter speed, and aperture directly impact image quality. ISO controls sensitivity to light, shutter speed determines motion blur, and aperture affects depth of field. Optimizing these settings for specific lighting conditions is crucial for sharp, well-exposed images and videos.
Principles of Composition and Framing

Effective aerial photography and videography rely on strong composition. Using the rule of thirds, leading lines, and other compositional techniques can significantly enhance visual appeal. Framing the subject effectively is crucial for creating impactful images.
Capturing Smooth Video Footage
Smooth video footage requires stable flight and potentially the use of a gimbal. Smooth, deliberate movements and avoiding sudden changes in direction are essential for professional-looking results.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning to safely and effectively pilot your drone is crucial, and a great resource to get started is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. This will equip you with the knowledge needed to confidently handle your drone and capture amazing aerial footage.
Planning and Executing Drone Photography Projects
Planning a drone photography or videography project involves creating a shot list, considering lighting conditions, and selecting appropriate camera settings. A well-defined plan ensures efficiency and helps achieve desired results. This includes scouting locations, identifying optimal shooting angles, and understanding lighting conditions to optimize image capture.
Drone Safety and Regulations
Understanding and adhering to local drone regulations and safety guidelines is crucial for responsible operation. This section covers key safety aspects and legal considerations.
Understanding and Adhering to Local Regulations
Drone regulations vary by location and often include restrictions on airspace, flight altitudes, and operational permissions. It is essential to research and comply with all relevant regulations before operating a drone.
Potential Risks and Risk Mitigation
Potential risks include collisions, battery failures, loss of control, and damage to property. Risk mitigation strategies include regular maintenance, thorough pre-flight checks, and careful flight planning. Maintaining awareness of surroundings and operating within one’s skill level is crucial.
Maintaining Safe Distance

Always maintain a safe distance from people, property, and obstacles during drone flights. This helps prevent accidents and ensures the safety of others. Following safe operating distances as Artikeld in local regulations is essential.
Common Drone Accidents, Causes, and Preventative Measures
| Accident | Cause | Preventative Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Collision with obstacle | Poor visibility, lack of situational awareness, inexperience | Thorough pre-flight checks, careful flight planning, maintaining awareness |
| Loss of control | Battery failure, GPS signal loss, malfunctioning components | Regular maintenance, using high-quality batteries, verifying GPS signal |
| Battery fire | Overcharging, improper handling, damaged battery | Proper charging practices, safe handling, regular battery inspection |
| Damage to property | Loss of control, collision | Careful flight planning, avoiding populated areas, maintaining awareness |
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are essential for keeping your drone in optimal condition and extending its lifespan.
Regular Drone Maintenance and Cleaning
Regular cleaning, inspecting propellers for damage, checking for loose screws and connections, and lubricating moving parts are crucial. A regular maintenance schedule helps to identify potential issues before they escalate into serious problems.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Problems
Common problems include low battery, GPS issues, motor malfunctions, and connectivity problems. Troubleshooting involves systematically checking components and connections to identify the root cause.
Replacing Drone Components
Replacing components such as propellers and batteries is often straightforward. However, always follow the manufacturer’s instructions to ensure proper installation and avoid damaging the drone.
Storing and Transporting a Drone
Proper storage and transport protect the drone from damage. Use a protective case or bag to prevent scratches and impacts during transportation. Store the drone in a dry, cool environment away from extreme temperatures and moisture.
Mastering the art of drone operation is a rewarding journey that combines technical skill with responsible practice. By understanding your drone’s capabilities, adhering to safety protocols, and respecting regulations, you can unlock a world of aerial exploration and creative possibilities. Remember that continuous learning and practice are key to becoming a proficient and safe drone pilot. So, take to the skies responsibly, and enjoy the breathtaking perspectives that drone technology offers.
FAQ Insights
What is the legal age to fly a drone?
The minimum age varies by country and region. Check your local regulations for specifics.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
It’s recommended to calibrate before each flight, especially if the drone has been moved significantly or experienced any impacts.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
Immediately switch to a lower-risk flight mode (like Attitude mode) and carefully land the drone in a safe location.
How do I handle strong winds during drone operation?
Avoid flying in high winds. If caught in unexpected winds, prioritize a safe landing, potentially using assisted landing features if available.
What is the best way to store my drone battery?
Store LiPo batteries in a fireproof bag, away from flammable materials, at a partially charged state (around 30-50%).
